Key Highlights
- Discover the rich nomadic heritage of Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, shaped by centuries of traversing the vast steppes of Central Asia.
- Learn about the importance of livestock and yurts, the traditional dwellings that provided shelter and mobility.
- Uncover the captivating history of Kazakh nomads, from their early origins to their resilience during Russian and Soviet rule.
- Immerse yourself in the vibrant cultural expressions, including traditional music, oral storytelling, and unique customs.
- Explore the challenges faced by contemporary nomadic communities and the efforts being made to revive and preserve their traditions for future generations.
Introduction
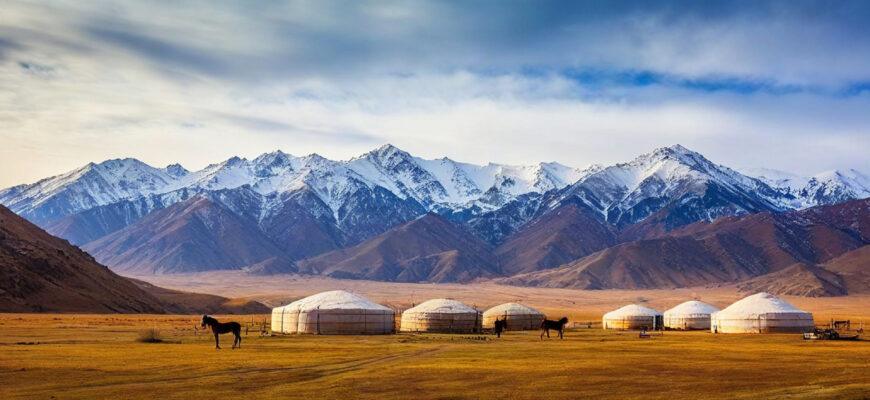
Kazakhstan is located in Central Asia and shares cultural ties with the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, as well as Mongolia and Russia. Its culture is deeply connected to its nomadic past. The Kazakh people lived as nomads for many years. They moved across the wide steppes, building a strong bond with the land and its resources. This rich heritage is still important today. It affects many parts of life, including food, music, social structures, and traditions.
The Essence of Nomadism in Kazakhstan
Nomadism in Kazakhstan is more than just a way of life. It shows a close relationship with nature, a strong respect for traditions, and a deep sense of community. This lifestyle values adaptability and resilience. These qualities have been shaped over many generations as people faced challenges in the steppe.
You can still see the strong influence of this nomadic tradition in Kazakh society today. It shows how this ancient way of life continues to affect people now.
What Defines Nomadic Culture?
Nomadic culture is known for its unique way of life that is closely connected to nature. People in these cultures are always moving, depending on the seasons and what resources are available. This travel means they often keep their belongings simple, focusing on what is useful.
A key part of this way of life is community. Nomadic groups usually have strong family ties and complex social systems that guide how they interact with each other and what responsibilities they have. Important values include respect for elders, being welcoming to guests, and sharing a strong sense of identity.
Traditional ways of life are kept alive through storytelling, music, dance, and skilled crafts. These forms of culture are not just fun to enjoy; they help pass on knowledge, history, and values from one generation to the next.
The Importance of Livestock and Mobility
Livestock, especially sheep and their wool, horses, and camels, is very important for the Kazakh nomadic way of life. These animals give food, materials for traditional clothing and shelter, and help with transportation. Herders know a lot about looking after these animals and how to use major ingredients from them. They change where they go based on what their flocks need.
Being able to move is key to survival in the steppe. The seasons change, pasture comes and goes, and water sources are sometimes hard to find. This nomadic lifestyle needs constant movement and helps people adapt, bounce back, and understand the land well.
Relying on livestock and the need to move shaped how Kazakh nomads live. It affected their economy, social life, cultural habits, and spiritual beliefs.
Historical Overview of Kazakh Nomads
The Kazakh steppe is a large area that goes from Eastern Europe to the borders of China, including the Tien Shan Mountains. It shows the deep history of the Kazakh nomads. For thousands of years, this land has been a meeting point for different cultures, with many nomadic groups shaping the region’s culture.
The Kazakh people began to become their own group in the 15th century. This was important for creating their special traditions and identity.
Early Origins and Historical Evolution
The Kazakh steppe has helped nomadic cultures for many years. Groups like the Scythians, Huns, and Turkic tribes have traveled these lands. They all left their marks on Kazakh history.
This region is important because it connects East and West. The Silk Road, which is a set of ancient trade routes, ran through the Kazakh steppe. This route helped people share ideas and customs, and it affected how civilizations grew.
In the 15th century, the Kazakh Khanate was formed. This was an important time in Kazakh history. It helped strengthen their identity and influence in the region. During this time, the Kazakhs developed their unique Turkic language, Kazakh language, culture, and traditions.
Impact of Russian and Soviet Rule on Nomadism
The Russian Empire expanded into Central Asia during the 18th and 19th centuries. This change had a big impact on the nomadic way of life in Kazakhstan and the number of Kazakhs. They started to practice settled agriculture. New administrative rules also contributed to the slow decline of traditional nomadism.
In the 20th century, Soviet rule changed nomadic practices even more. Collectivization programs tried to modernize agriculture. This made many nomadic families settle down, disrupting their livestock herding habits.
Despite these tough times, the Kazakh people kept their national identity. They also preserved many parts of their cultural heritage.
Key Aspects of Nomadic Life
To understand the Kazakh nomadic culture, we need to look at the main things that shaped their daily life. Their unique yurts were like homes they could move easily. Horses were also very important for their journeys. These points show us their way of life.
Looking into these features helps us see how they adapted to their surroundings and the cultural meaning behind these parts of their life.
Yurts: The Traditional Nomadic Home
The yurt is a portable home made of felt and wood. It shows the smartness and flexibility of Kazakh nomads. These round homes are great for life on the move. They offer easy transport and protection from bad weather.
Inside the yurt, you can see practicality and tradition. It has special spaces for different activities, showing a real respect for order and customs. The right side is usually for men. The left side is for women, while guests and family members have specific spots.
Yurts are not just homes; they show the kindness and hospitality of Kazakh culture. They are also places for gatherings, celebrations, and sharing traditional Kazakh cuisine.
Role of Horses in Nomadic Lifestyle
Horses are very important in the Kazakh nomadic lifestyle. They are companions, ways to travel, and symbols of status. The Kazakh people have a strong bond with horses. They appreciate their strength, speed, and loyalty.
Horseback riding is more than just a way to get around; it is a skill that is celebrated and brings pride, just like the early steps representing the legs of a child. Traditional games like Kyz Kuu, known as ‘Chase the Girl,’ show the skill of riding and the importance of staying in the saddle, as well as the significance of horses in Kazakh culture, similar to those enjoyed in Kyrgyzstan.
Horses have had a big impact on the identity and traditions of the Kazakh people. They have been key in their travels across the vast steppes and in their cultural expressions, including their use of horse meat and a variety of dairy milk products in traditional dishes, like the most popular Kazakh dish, Besbarmak.
Social Structure and Traditions
The nomadic way of life for the Kazakh people helped build a strong community and complex social groups. These groups, based on family connections and tribal links, created order, teamwork, and a feeling of belonging.
Knowing these social dynamics is important for understanding the values that guide actions, shape customs, and keep peace in Kazakh society.
The Clan System and Tribal Hierarchy
The clan system is very important in Kazakh society. It helps people connect, organize, and support each other. Each clan can trace its roots back to a common ancestor. This creates a strong sense of family and shared history.
In this system, there is a tribal ranking that affects a person’s social status and how they interact with others. This ranking is flexible. People can earn respect through their personal traits like wisdom, generosity, and bravery, not just their family background.
The clan system and tribal hierarchy touch many parts of Kazakh life. They affect how people marry, inherit property, and resolve conflicts.
Marriage, Family, and Kinship in Nomadic Societies
Marriage in Kazakh nomadic societies is not just about two people coming together; it is also about joining two families and clans, especially during the first wedding party, which can be seen as a literal translation of social unity. Families, including the relatives of the groom, play a key role in choosing partners by looking at social standing, family history, and how well the families match.
Family units are usually very close, often including many generations living under one roof. It is very important to respect elders. Their advice is trusted when making decisions and passing down traditions.
Kinship goes beyond just immediate family. There is a strong focus on helping each other and being friendly within the clan. This network of close relationships is very important for surviving in the tough conditions of the steppe.
Cultural Expressions of Kazakh Nomads
The artistic spirit of the Kazakh nomads shows through different forms. This includes the beautiful tunes of their traditional music and the interesting stories in their oral literature. These expressions share their history, beliefs, and the beauty in their surroundings.
When we explore these artistic traditions, we can see the depth and richness of Kazakh culture. It highlights a people who celebrate their heritage through words and sounds.
Traditional Music and Instruments
Traditional Kazakh music captures the feeling of the steppe, highlighting the connection the Kazakh people have with their land in the United States. Its melodies are haunting, and the rhythms are detailed. The music reflects the life of nomads, showing joy, celebration, and the sadness of long trips.
One important musical instrument is the dombra. This is a two-stringed lute used in solo and group performances. Its special sound can take listeners right to the Kazakh steppe.
Through music and folklore, the Kazakh people keep their history alive. They share their values and stories, making sure these traditions continue for future generations.
Oral Literature and Storytelling
Oral literature is very important in Kazakh culture. It acts as a store of wisdom, history, and entertainment. Skilled storytellers, called “zhyrau,” hold audiences’ attention with epic tales about heroes, mythical creatures, and the nomadic way of life.
These stories are not just for fun. They are a form of poetic art that keeps history alive, teaches values, and helps form a shared identity. The rhythmic verses and bright images take listeners to other worlds, sparking their imagination.
Even as the world modernizes, the art of oral storytelling still shines in Kazakhstan. This keeps the stories and their cultural heritage alive for future generations.
Religious Beliefs and Practices
The religion in Kazakhstan is a mix of old beliefs and major world religions. Shamanism has been around for a long time, and Islam is widely accepted, especially among ethnic Kazakhs. These beliefs show us the spiritual life of the Kazakh people.
When we look at their religious practices, we see how much they respect the divine, their ancestors, and nature.
Shamanism and Ancestor Worship
Shamanism is an old belief system that came before most big world religions, and it holds historical significance in Kazakh culture. It has influenced Kazakh culture a lot. Shamans are seen as special people who connect the living with the spirit world. They were called upon for help, guidance, and to talk to spirits.
In Kazakh traditions, worshiping ancestors is very important. People show respect for their elders, and they also believe that the spirits of their ancestors still affect the lives of the living. To honor them and share good news, they make offerings and perform rituals to seek their blessings.
These beliefs show that people think of themselves as part of both the natural and spiritual worlds. Respecting the balance between these two worlds is essential for living in harmony.
Influence of Islam on Nomadic Traditions
Islam came to Kazakhstan around the 8th century. It slowly spread and mixed with the beliefs that were already there. The nomadic lifestyle had some challenges for following Islamic rules closely. This led to new ways of worship that mixed different traditions.
Even though people accepted Islam, many nomadic customs stayed and blended into the new religion. Values like hospitality, respect for elders, and the importance of family and community remained key.
Today, Islam is still important in shaping how many Kazakhs think and act in their daily lives and culture.
Contemporary Nomadism in Kazakhstan
Modernization has changed Kazakhstan a lot, but signs of its nomadic past still exist, especially in rural areas where people keep their traditional ways. Today, nomadic life has challenges in the 21st century.
Still, more people are working to bring back and protect these traditions. They see the value of nomadic culture and the important lessons it provides in a fast-changing world.
Modern Challenges Facing Nomadic Communities
Contemporary nomadism in Kazakhstan has serious challenges. Economic pressures, climate change, and the appeal of city life have caused fewer people to be nomadic herders. Keeping traditional livestock practices in today’s global economy is a hard task.
Climate change brings problems like desertification and lack of water. These impact the nomadic way of life. Nomadic herders depend on stable weather and natural resources. When the environment suffers, their livelihoods and traditional ways are at risk.
Even with these problems, many nomadic communities are strong. They adapt to new situations while working hard to keep their cultural heritage alive for the coming generations.
Revival and Preservation of Nomadic Culture
In recent years, a strong effort in Kazakhstan has focused on bringing back and keeping nomadic culture alive, highlighted by the World Nomad Games which include traditional sports such as horseback archery and eagle hunting. Festivals, museums, and educational programs are helping people see why this heritage is important.
People are working to support traditional skills like felt making and yurt construction. This helps keep these skills alive and preserves cultural knowledge. These projects also help improve the economy of nomadic communities while keeping their traditions strong.
Bringing back and protecting nomadic culture honors history. It gives us helpful ideas about living sustainably, being resilient, and the lasting connection between people and nature.
Conclusion
Kazakhstan’s nomadic history is a big part of its culture. Nomadism shows itself in traditions like yurts and the use of horses. Even with modern problems, people are still working to keep nomadic culture alive. The clan system, traditional music, and religious beliefs are key parts of Kazakh nomadic heritage. Knowing how nomadic communities have changed over time helps us see why it matters to keep these traditions. Share the beautiful story of Kazakhstan’s nomadic roots on social media to honor and highlight this special cultural legacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How have Kazakh nomadic traditions influenced modern Kazakhstan?
Kazakh nomadic traditions still play a big role in the national identity of modern Kazakhstan. They shape its food, music, social values, and cultural practices, including a large practice of salting meat for preservation, as well as a preference for sour milk. This lasting influence is well-known for its focus on being hospitable, honoring elders, and building strong community connections, with the most common Kazakh rice dish often being a highlight at gatherings.
What are the main components of a traditional Kazakh yurt?
A traditional Kazakh yurt has a wooden frame that is covered with felt. It is made to be easy to move and flexible. The yurt’s round shape, the opening at the top, and its detailed decorations show how useful it is and how important it is to the culture.
How is the clan system relevant in today’s Kazakh society?
The clan system is not as strong as it used to be, but it still matters in modern Kazakh society. It shapes how people interact, how they marry, and their shared sense of identity, especially in rural areas.
What role does traditional music play in nomadic rituals and ceremonies?
Traditional Kazakh music is very important in nomadic rituals and ceremonies. It is used during celebrations, times of sorrow, and storytelling. This music helps to keep cultural heritage alive and build strong connections within the community.









